Among all City departments, RAP is the largest employer of part-time employees. As full-time employment has decreased, RAP has increasingly relied on part-time staff to take on greater responsibilities. RAP’s part-time staff budget has remained nearly constant over the past 15 years. Over the same period, the part-time personnel costs have increased per-employee. For context, in 2009, the minimum wage in California was $8 per hour.2“History of California Minimum Wage,” State of California Department of Industrial Relations, 2025. In 2015, the City of Los Angeles adopted a $15 per hour minimum wage.3“LA City Council Votes To Raise Minimum Wage To $15 By 2020,” National Public Radio, May 19, 2015. As of 2025, the minimum wage in the City of Los Angeles is $17.87 per hour. Hourly minimum wages effectively doubled between 2009 and 2015 although the RAP budget for part-time personnel has remained relatively constant. As a result, RAP has fewer hours of part-time work annually.
Impact of Staffing and Budget Cuts on Operations & Maintenance
Interviews with RAP staff revealed the following challenges resulting from budget constraints.
- RAP’s operating resources are declining despite responsibilities growing. RAP staff are being asked to do more with less, leading to staff burnout, deferred maintenance, and growing waitlists for programs. For example, recreation centers used to have staff on Sundays, but now do not as a result of a strained budget. Anecdotally, RAP staff discussed a decline in maintenance quality due to lower staffing and less frequent visits to service parks. Staff also shared that RAP switched from a system of dedicated gardener caretakers for each park to a system where staff visit parks on rotation within a district.
- RAP faces recruitment and retention difficulties due to limited resources and lower wages compared to other departments. RAP provides pathways into City services with part-time positions and established onboarding and training practices. Agencies like the Department of Water and Power and the Port of Los Angeles offer higher salaries and more overtime opportunities, making it difficult to retain staff after RAP trains skilled positions.
- Deferred maintenance is increasing, resulting in greater long-term costs.With a focus on essential tasks like litter removal, restroom cleaning, and landscaping; other necessary upkeep is often delayed, leading to more expensive repairs and increased City liability over time.
- RAP is responsible for providing shelters during emergencies, creating additional and unpredictable workloads for staff. As extreme events increase in intensity and frequency, this will be a growing role for RAP within the city.
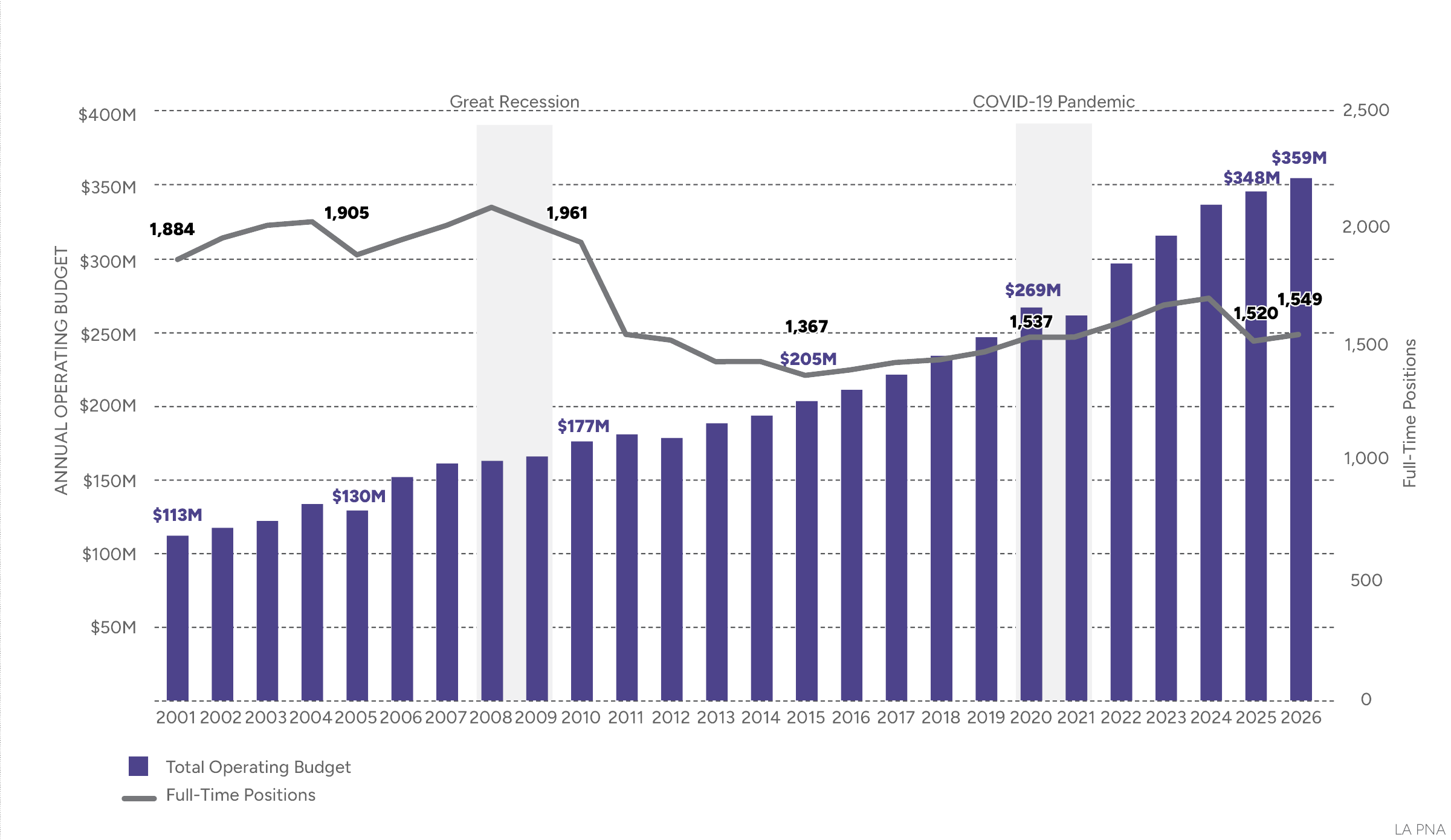
- Over the long term, during economic downturns, RAP staff positions are eliminated more quickly and in larger numbers than they are recovered. Vacant full-time positions continue to be eliminated in budgets year-over-year. Between FY 2024 and FY 2025, 207 vacant full-time positions were eliminated or discontinued, further straining RAP’s operating needs.
Sources
- 1Full-time positions refer to full-time authorized positions according to data provided by RAP.
- 2“History of California Minimum Wage,” State of California Department of Industrial Relations, 2025.
- 3“LA City Council Votes To Raise Minimum Wage To $15 By 2020,” National Public Radio, May 19, 2015.

![RAP has less than half the authorized positions today as it did before the Great Recession.[mfn]Part-time employees do not equate to full-time employees, but total number of part-time employees. This chart does not include staff funded by administrative allocations from special funds such as Quimby.](https://needs.parks.lacity.gov/wp-content/uploads/full-and-part-time-staff-positions.png)